User report on gene marker contextualization – Disease models meet genetics
The knowing01 app is distinguished by its ability to effectively enrich marker gene identification efforts by enabling researchers to go beyond traditional bioinformatics tertiary analysis.
We often face the challenge of being tasked with selecting the disease-relevant markers from a set of ten to hundreds of candidate genes or proteins from transcriptomics or proteomics analyses. While you may consult a bioinformatician to look for overlaps or manually work through five or more Excel sheets, it is time consuming (although it shouldn’t be) as it is a highly repetitive task.
Worse, it is prone to errors, especially when manually comparing gene names across species or cross-referencing genetic data with transcriptomics analysis results.
This can be automated!
One of our first users’ research on psychiatric disorders exemplifies this automation by using our knowing01 app. She overlaid transcriptomics results from mouse and rat models with multiple human GWAS datasets and enriched the findings with transcription factor data. As a neurobiologist, she worked hands-on with our easy-to-use web app to integrate, explore, and contextualize marker candidates.
This targeted, easy, and automated approach enabled her to prioritize genes for experimental validation that are not only statistically associated with the disorder but also biologically significant.
The ingredients for this recipe of success
In the field of genomics, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have become an indispensable tool for identifying genetic variations associated with certain diseases. However, these studies generate enormous amounts of data, and sifting through these datasets to pinpoint the truly important genes can be challenging.
In the field of disease models, genetically altered mouse models are often created to study the molecular underpinnings of human diseases. Sampling diseased tissues from these models and subjecting them to omics measurements is the method of choice. However, once the data is analyzed, the key question remains: Which of these molecular changes are also observed in the corresponding human disease?
This is where the knowing01’s solution comes into play.
In this blog post, we will explore how our solution enables groundbreaking research, focusing on the recent findings of an early user from Munich, Dr. Lotte van Doeselaar, during her PhD research on psychiatric disorders.
The work: A Deep Dive into Gene Regulation and Psychiatric Disorders
For her doctoral thesis on stress resillience, Lotte van Doeselaar used the software from knowing01 to explore the molecular underpinnings of stress resilience as follows:
By systematically overlaying differentially expressed genes from mouse and rat disease models, co-expression networks and transcription factor enriched genes with data from human psychiatric GWAS studies [1], she identified key hub genes within complex gene networks. Her research sheds new light on the complex genetic architecture behind these disorders and offers potential avenues for developing therapies.
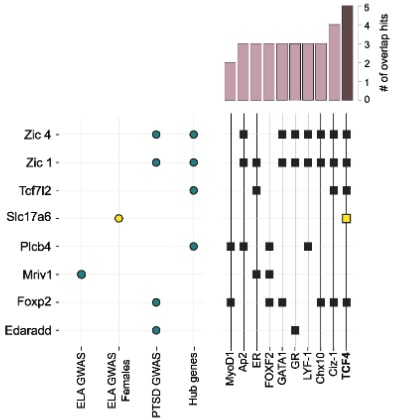
She used knowing01‘s software to identify transcription factors that could drive these gene networks. She compared datasets from GWAS studies of PTSD and childhood trauma survivors and overlaid them with her hub gene network to identify highly connected genes with regulatory potential. This analysis revealed that eight genes regulated by enriched transcription factors were consistent with both the GWAS and hub gene data. Among these, transcription factor 4 (TCF4) emerged as a significant driver, regulating five key genes – Foxp2, SLC17A6, Tcf7l2, Zic1, and Zic4. Remarkably, TCF4 has been linked to childhood trauma in females, suggesting a role in gene-environment interactions, particularly between early-life stress (ELS) and the Fkbp5 genotype. This multi-layered analysis, made possible by knowing01, empowers researchers to explore both the genes of interest and the regulatory factors influencing these networks.
Selected key findings and implications of the thesis:
Enhanced gene discovery: By using our software to overlay regulated genes with GWAS data, van Doeselaar discovered genes that might have been missed by conventional analyses. This enhanced discovery process is crucial to advance our understanding of complex traits and diseases.
Transcription factor focus: The thesis showed that enriched transcription factors can serve as a valuable data layer to filter and highlight the most relevant genetic variation. This enrichment process improves the entire discovery pipeline, making it more efficient and effective.
Congratulations, Lotte, on your important work!

Making Research Life Easier with knowing01
The approach Lotte van Doeselaar uses in her work is not limited to psychiatric disorders. Her methodology and the capabilities of knowing01 can be adapted to a variety of genetic, homology, disease and therapie research areas.
It unlocks new possibilities for revealing validated key marker complex traits and diseases in silico. By shedding more light on gene regulation and interaction, the knowing01 platform provides a robust toolkit for mapping genetic interactions with greater clarity and precision.
Our solution addresses this issue by combining data integration, advanced MutliomicsAI algorithms, and a user-friendly interface, making high-level genetic research more accessible. Researchers using knowing01 can not only explore these huge datasets more efficiently, but also gain deeper insights into gene function and interaction.
Ready to contextualize candidate genes, proteins or variants?
If you are facing challenges in your research, knowing01 is here for you. Our software and dedicated support team can help you with complex data analysis, integration of different data sources, and more. Contact us today to learn how knowing01 can help you make groundbreaking discoveries.
Book a demo with us or use the contact form below.
[1] GWAS of childhood traumatic events (Warrier & Baron-Cohen, 2021) from UK Biobank and GWAS of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD; Nievergelt et al., 2019) and major depression (MDD; Wray et al., 2018) from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC).